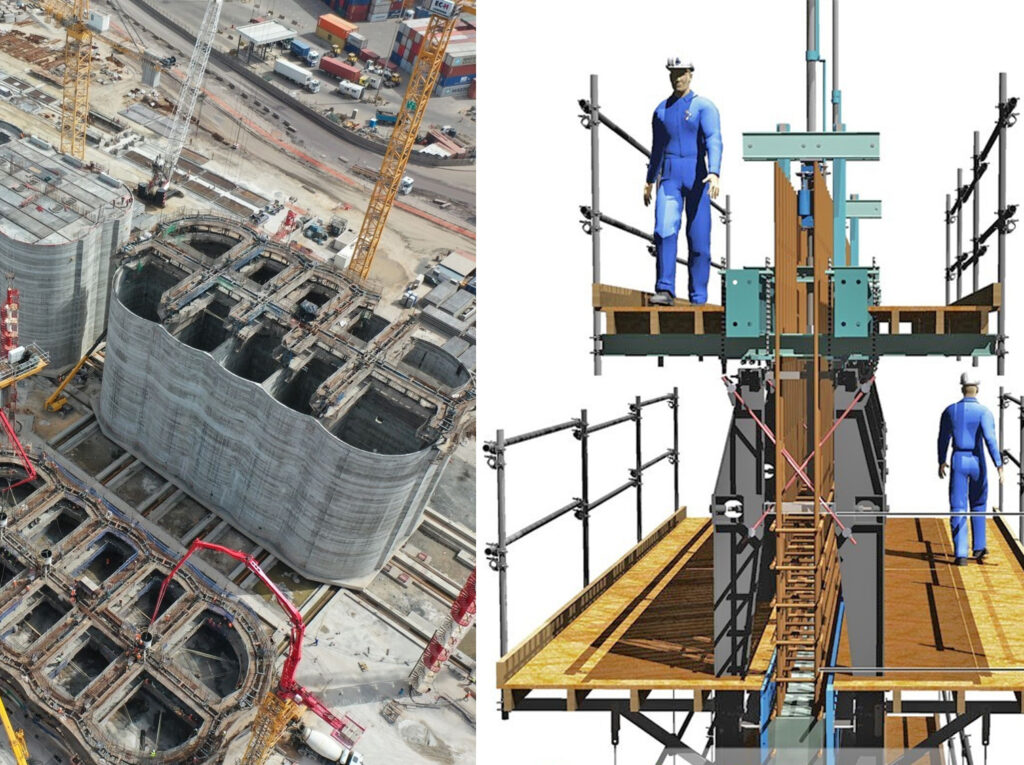
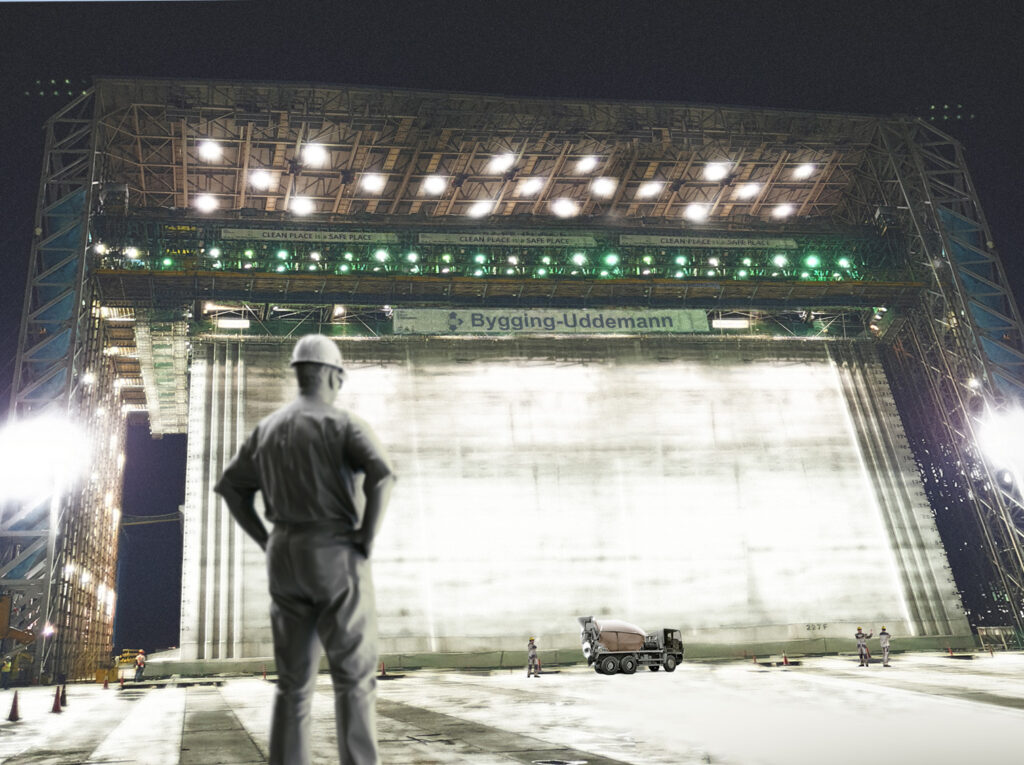
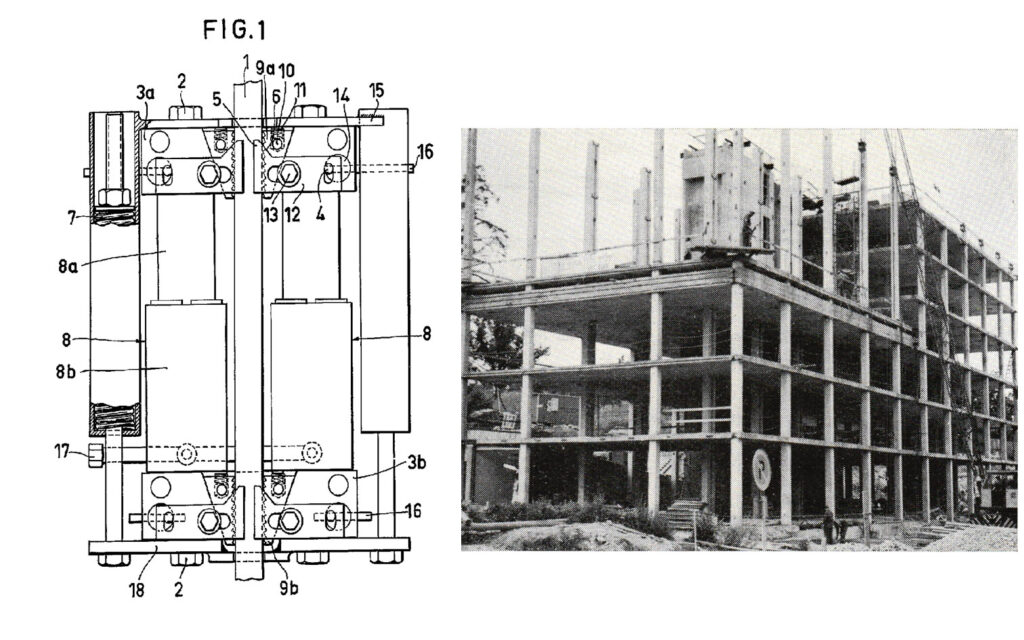
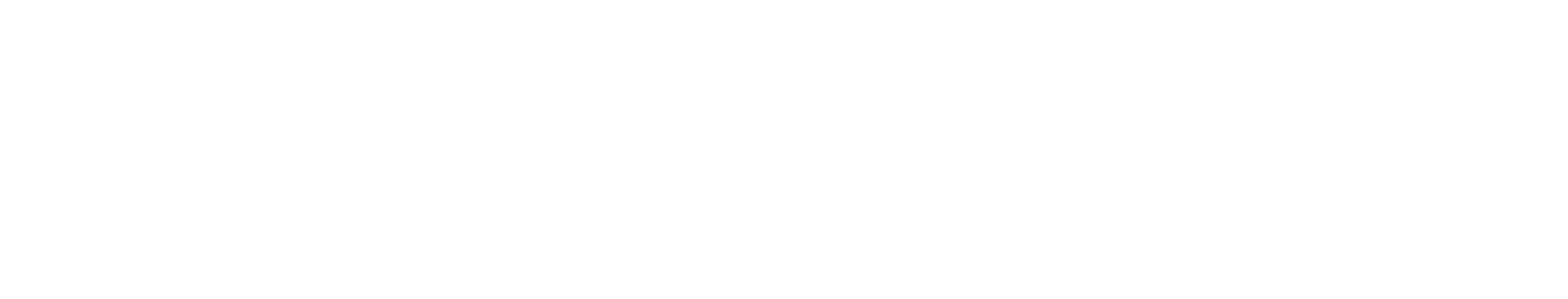Invention of the Hydraulic Slipform Jack
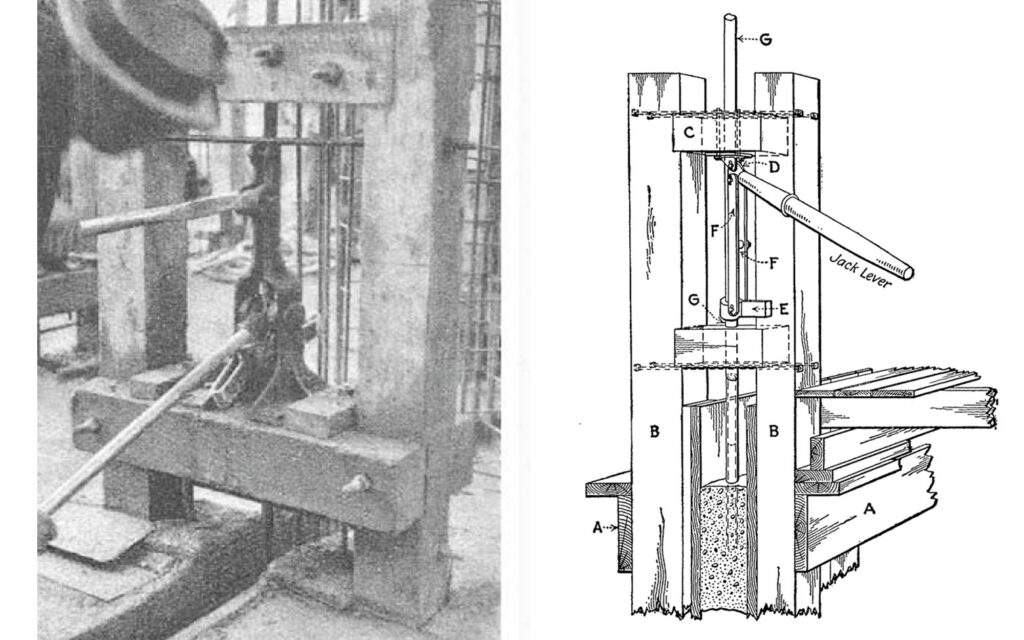
The first experiments with a hydraulic slipform jack was performed 1943. The lifting equipment consists of a number hydraulic jacks, connected to an oil pressure pump. The pump is calculated to serve up to 75 jacks and can be controlled and operated by a single person.
Patent registered to Erik von Heidenstam and Emrik Lindman, AB Byggförbättring, 1944.
The invention of the jack was soon followed by the elaboration of a series of other ancillaries, such as a universal yoke and steel form, which can quickly be assembled and dismantled. This fully mechanised and fully automatic slipform technique became known as “the Concretor-Prometo System” or “the Swedish Slipform Method”.
First hydraulic slipform equipment delivered abroad
After development on the domestic market, the first slipform equipment was delivered abroad in 1947.
The company was experiencing an explosive demand for the technology in Sweden and neighbouring countries. In half a decade, the company’s hydraulic slipform technology has been used for the construction of over 300 silos and grain terminals.
First residential building in the world raised by slipforming
The first residential building in the world, a seven-storey building in Västertorp, Stockholm, Sweden, was built using slipform technology.
Uddemann Byggteknik AB is founded
Uddemann Byggteknik AB (a.k.a. Uddeholm-Mannesmann Byggnadsställningar AB) was founded in Stockholm, Sweden.
Initially, the company operated in the design and manufacture of scaffolding. In 1965, the company changed its name and expanded its operations to include slipforming and heavy lifting.
Slipforming of Hydropower plants
Our slipform technology has been used in the construction of a large number of hydropower plants in Sweden. Examples are: Forsmo, Grundfors, Lasele, Ligga, Långbjörn, Näverede, Porsi, Stensele, Stenungsund, Stornorrfors, Umluspen and Vargfors. The picture shows slipforming of the arch dam at Vargfors, Sweden, 1958.
Development of heavy lifting
AB Bygging was granted a patent for a climbing jack for heavy lifting, which was the starting point for the development of our jacks in the 2510 series. The following year, these jacks were used during the construction of the “Läkarhuset” in Solna Centrum. First, the stairwell shafts were slipformed, then the floor slabs were lifted into place by the climbing jacks. The construction procedure is known as the Youtz-Slick-method or Lift slab construction.
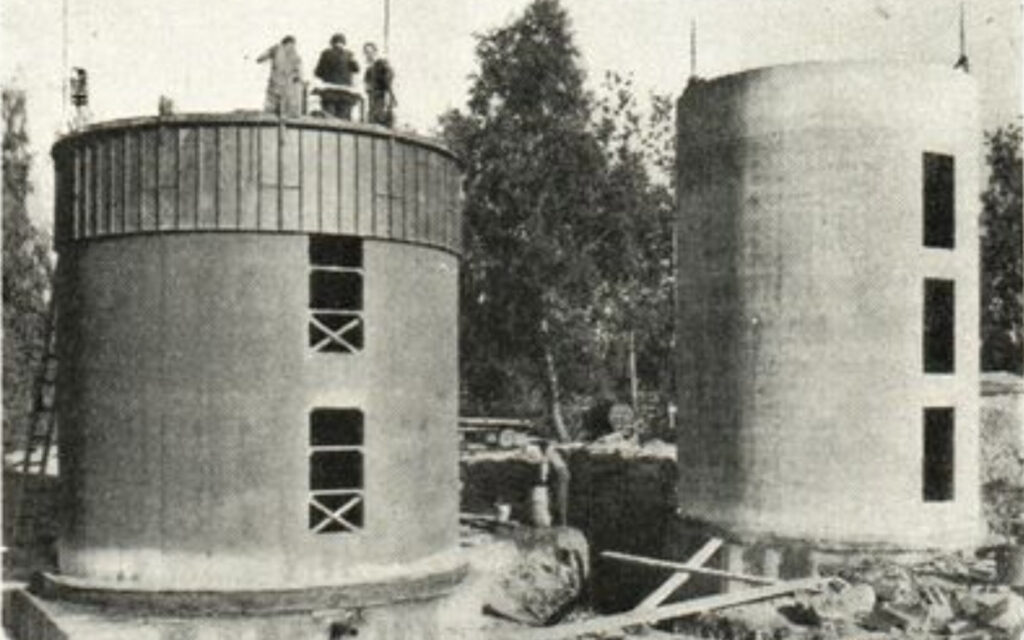
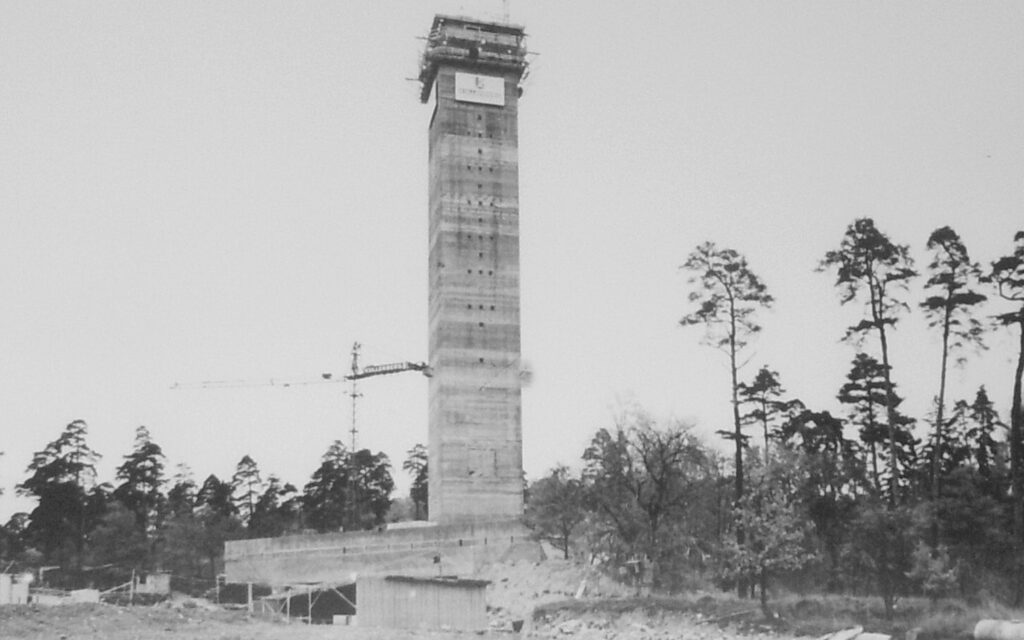
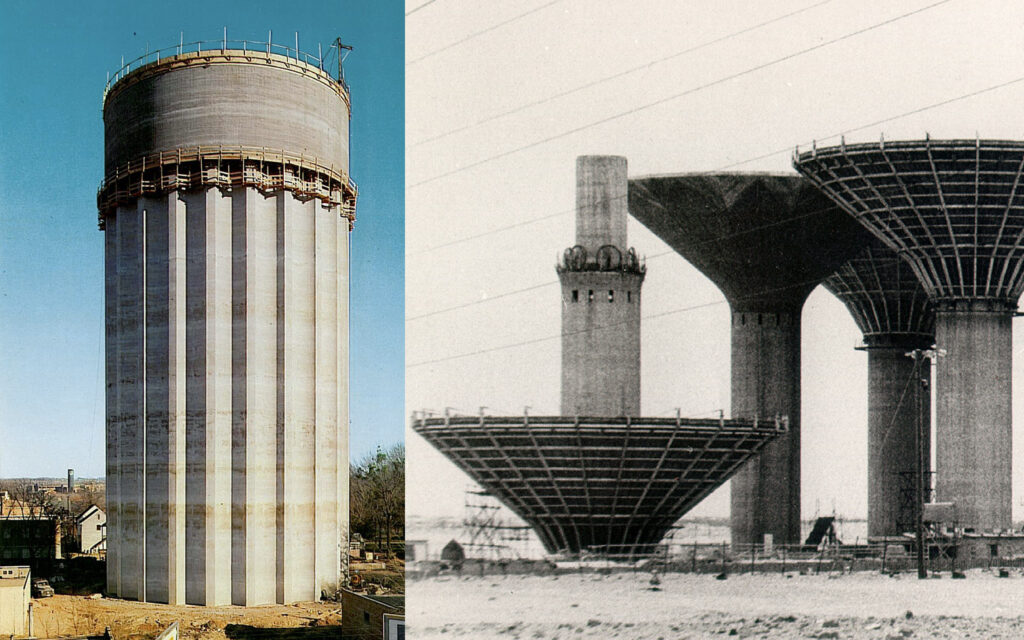
Methods for construction of Water Towers
Over the years, the company’s technology has been used to build hundreds of water towers around the world.
During the early 1960s, our method for the construction of mushroom-shaped water towers was developed. In step one, the shaft is slipformed, then the water reservoir is cast on the ground. In a final step, the reservoir is lifted – with our equipment for heavy lifting – and anchored to the top of the shaft.
The first picture shows a water tower in Tyler, Texas, US. The other shows several water towers in Kuwait city. (During the project, a total of 31 water towers were built at various locations in Kuwait.)
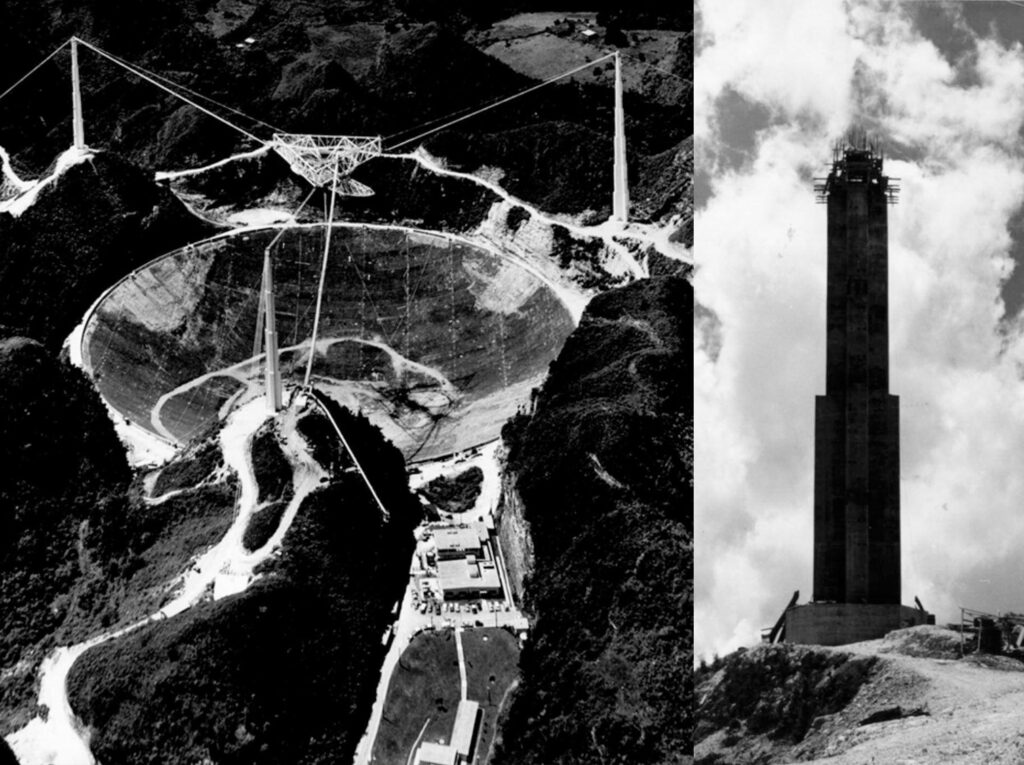
Towers for the Arecibo Telescope, Puerto Rico
Technique for slipforming of the three supporting towers.
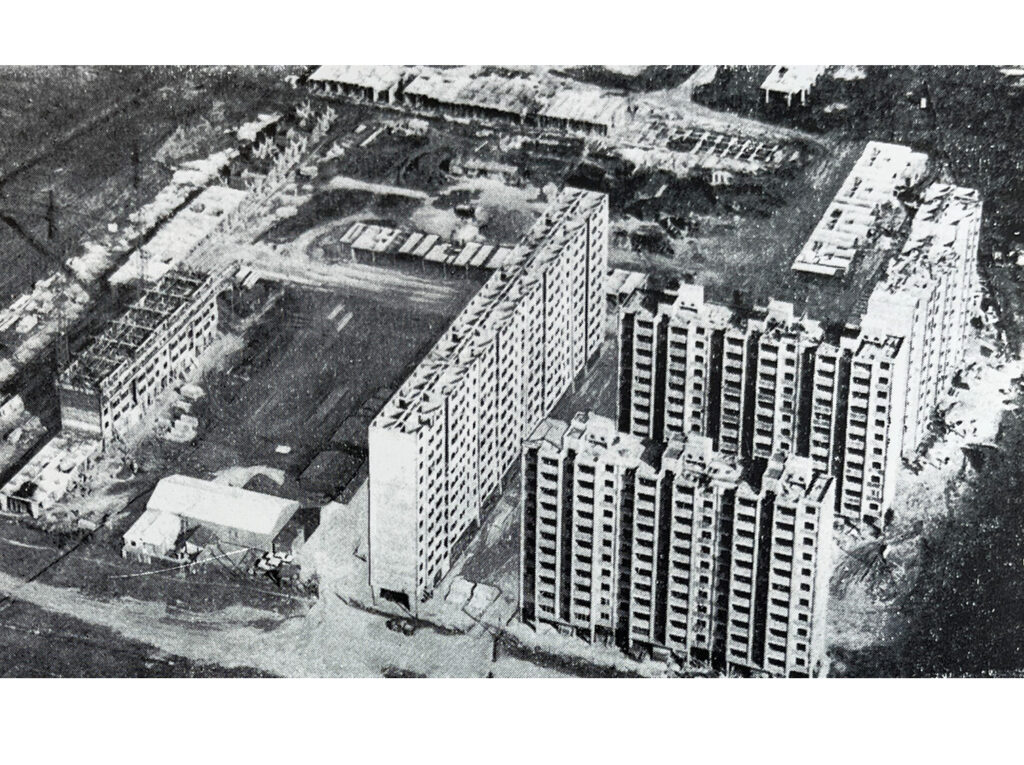
Slipforming of residential block, Buenos Aires, Argentina
A block of residential buildings (a total of 1302 apartments) was built using our expertise and technology.
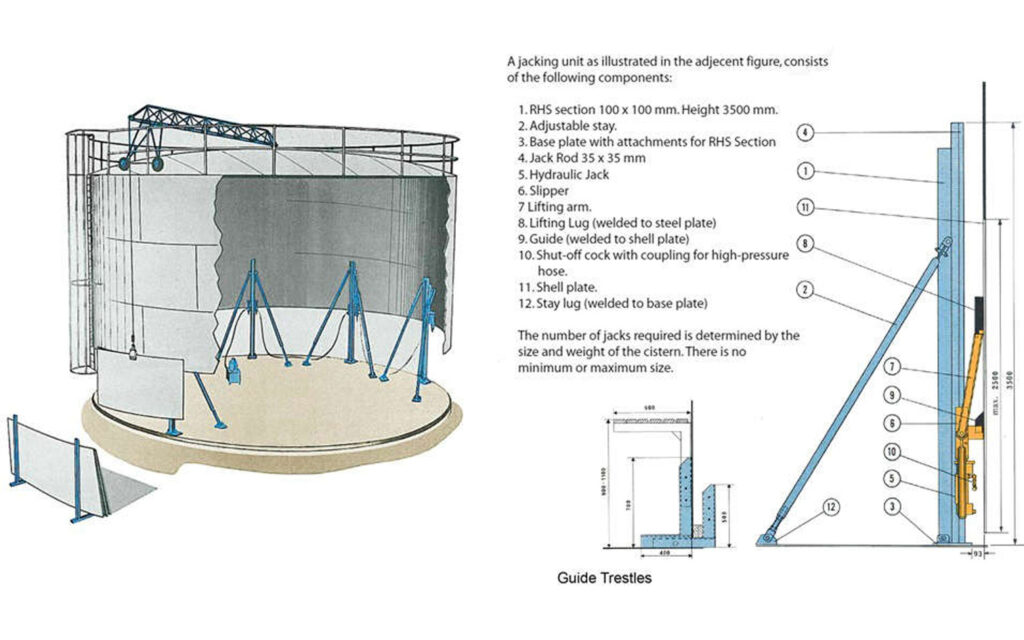
Revolutionary method for constructing cisterns and steel tanks
During the 1960s, our method for steel tank construction was developed. The principles of the method are that the steel tank is built from top to bottom, all at foundation level. The steel tank is lifted in stages using our climbing jacks (2510-series) mounted on lifting trestles, positioned inside and along the circular wall.
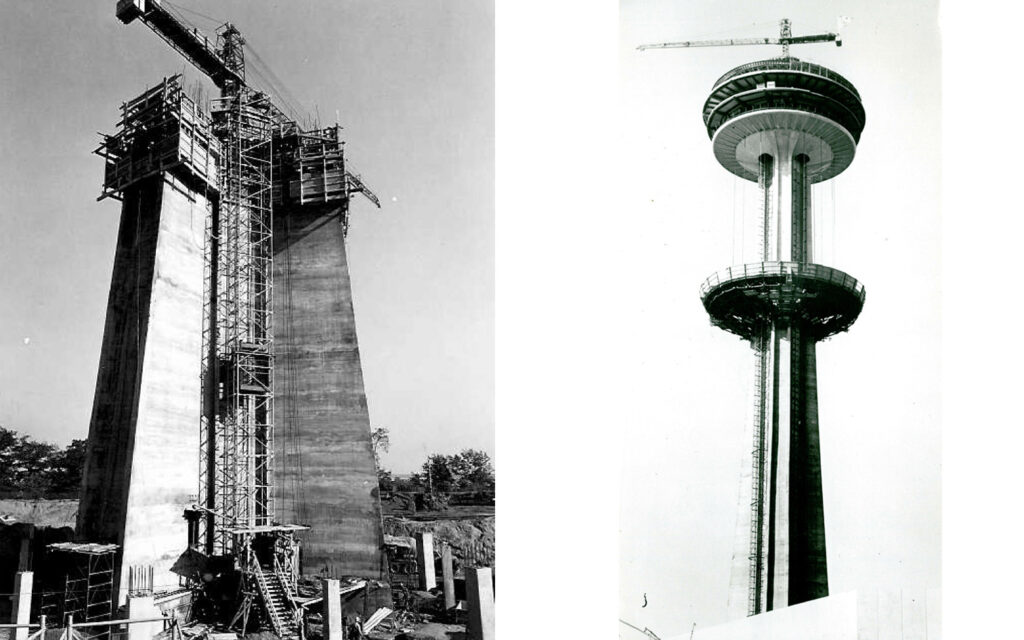
Kaknästornet, Stockholm, Sweden
Slipforming of observation tower “Kaknästornet”, Stockholm, Sweden
Height 155 metres.
Skylon Tower, Niagara Falls, Canada
Slipforming of the main shaft (125 meters) and heavy lifting of formwork for the observation deck (160 tons).
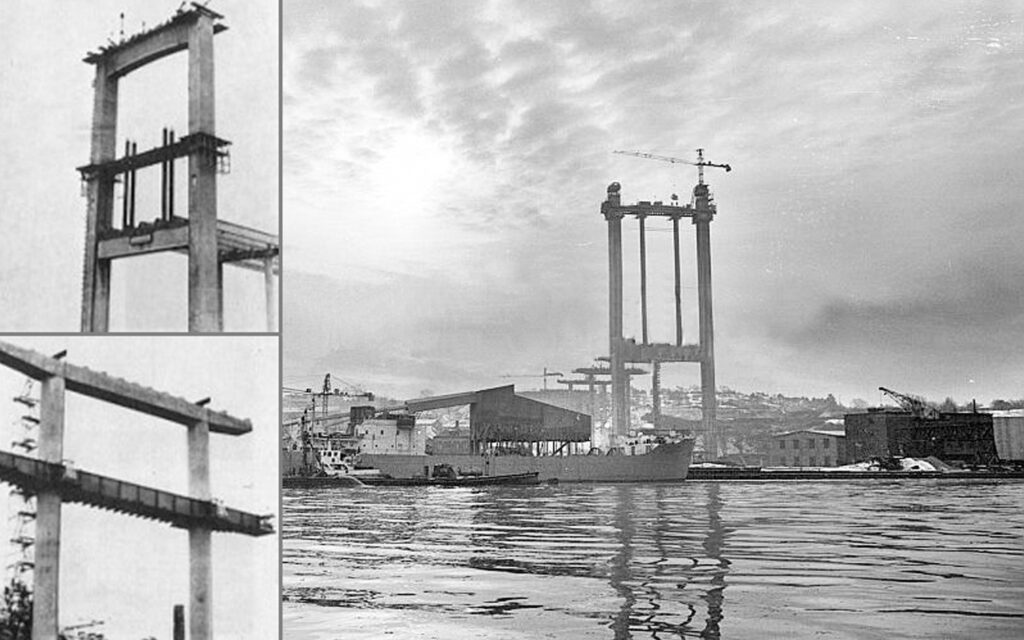
Älvsborgsbron, Gothenburg, Sweden
Slipforming of columns and piers for the approach viaducts, the cable anchors and bridge pylons. Raising and lowering of formwork for cross beams on the bridge piers.
Patent for Conical Slipform System
In 1965, the company was granted a patent for a slipform system for conical structures “The Svetho System”. The development of the method took place in collaboration with the Hungarian state construction company ÁÉV 31.
Prescribed changes to design parameters, such as diameter and wall thickness, are checked in all units simultaneously.
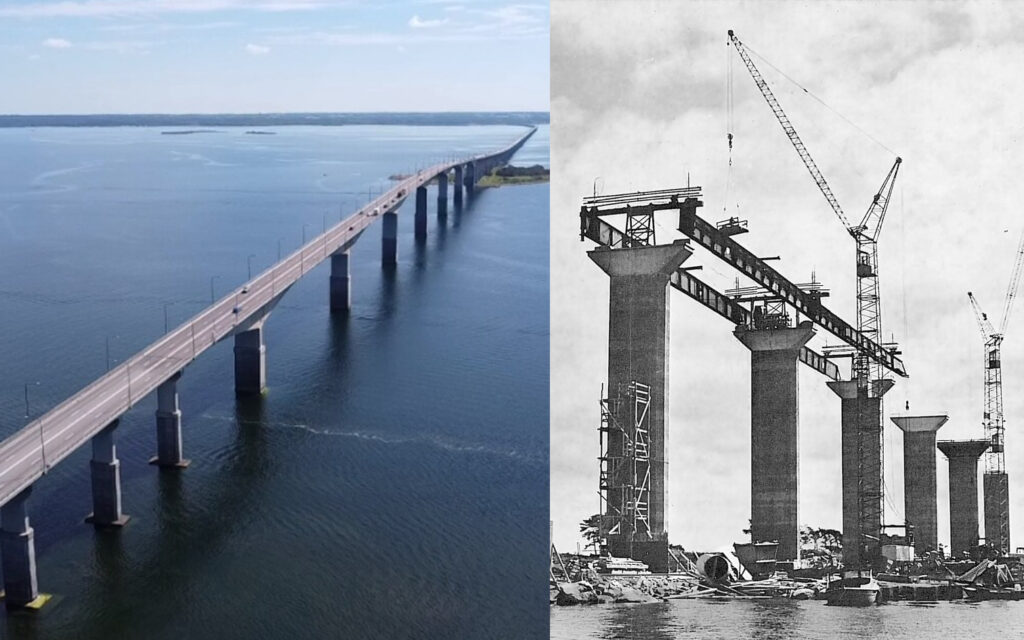
Ölandsbron, Slipforming and Heavy lifting, Sweden
Slipforming of pillars for Ölandsbron, Sweden, as well as raising/lowering the formwork of the bridge deck.
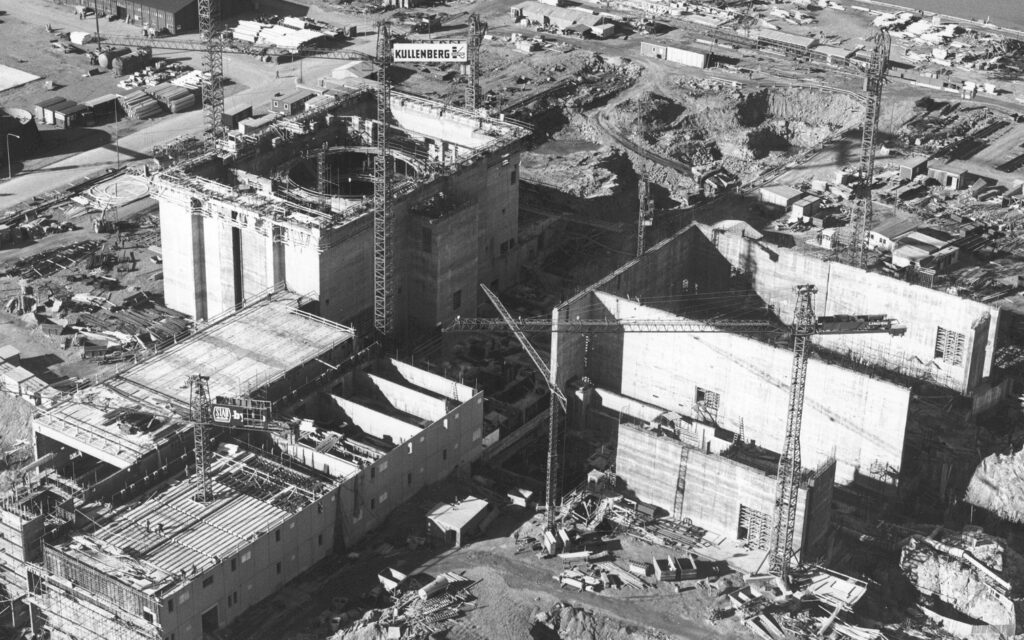
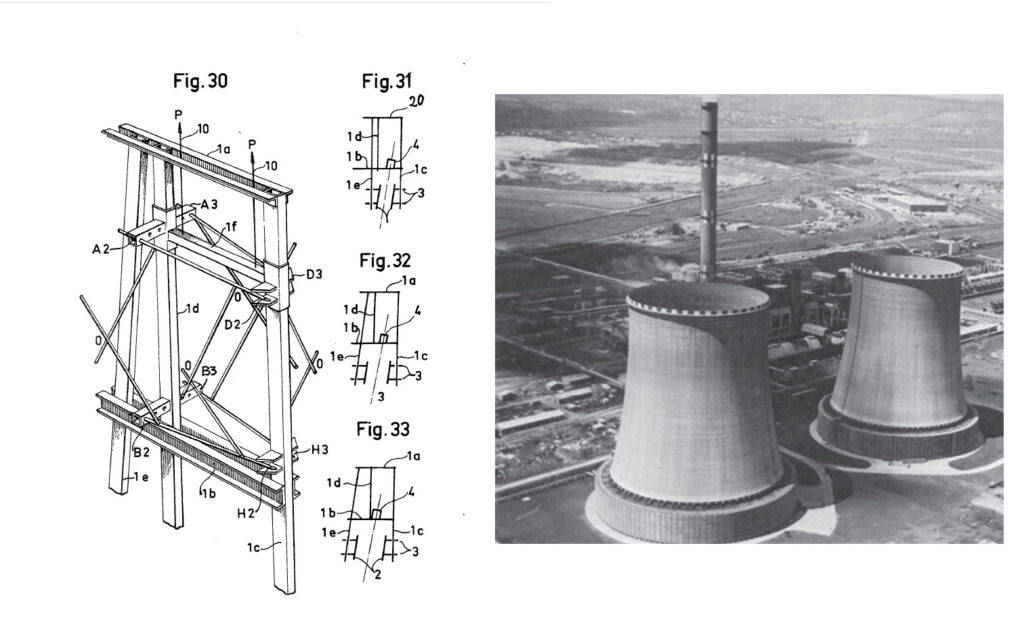
Slipforming of Nuclear Power plants
Slipforming of walls for nuclear power plant Ringhals, Sweden, and later also Forsmark, Sweden and Loviisa, Finland.
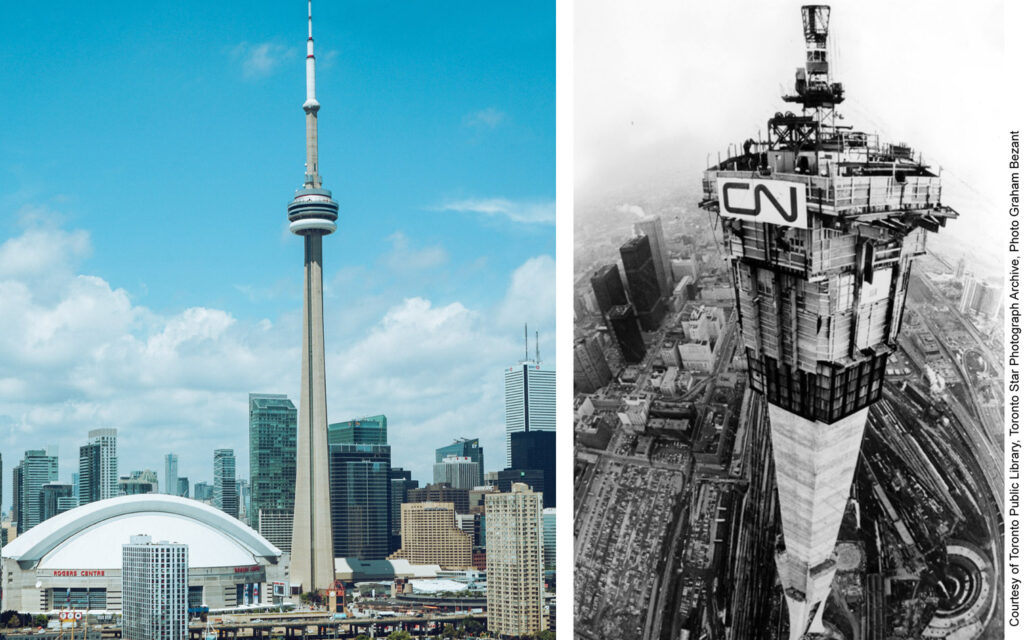
CN-tower, Toronto, Canada
Hydraulic technology for raising the slipform and heavy lifting of the work platform for the SkyPod.
Total height 553 m, slipformed up to level 446 m. The CN-Tower held the record for the world’s tallest free-standing structure for 32 years, from 1975 until 2007, when it was surpassed by the Burj Khalifa.
Read more here!
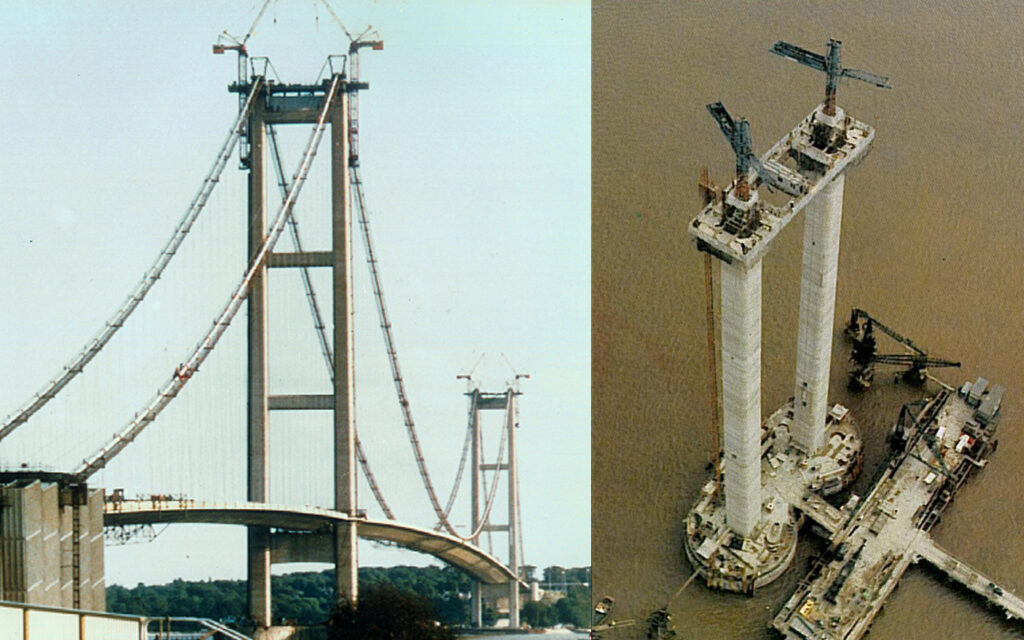
Humber Bridge, Kingston upon Hull, UK
Slipforming of pylons for the Humber Bridge. Height 155 meters.
When it opened, 24 June 1981, the bridge was the longest single-span road suspension bridge in the world, not surpassed until 1998.
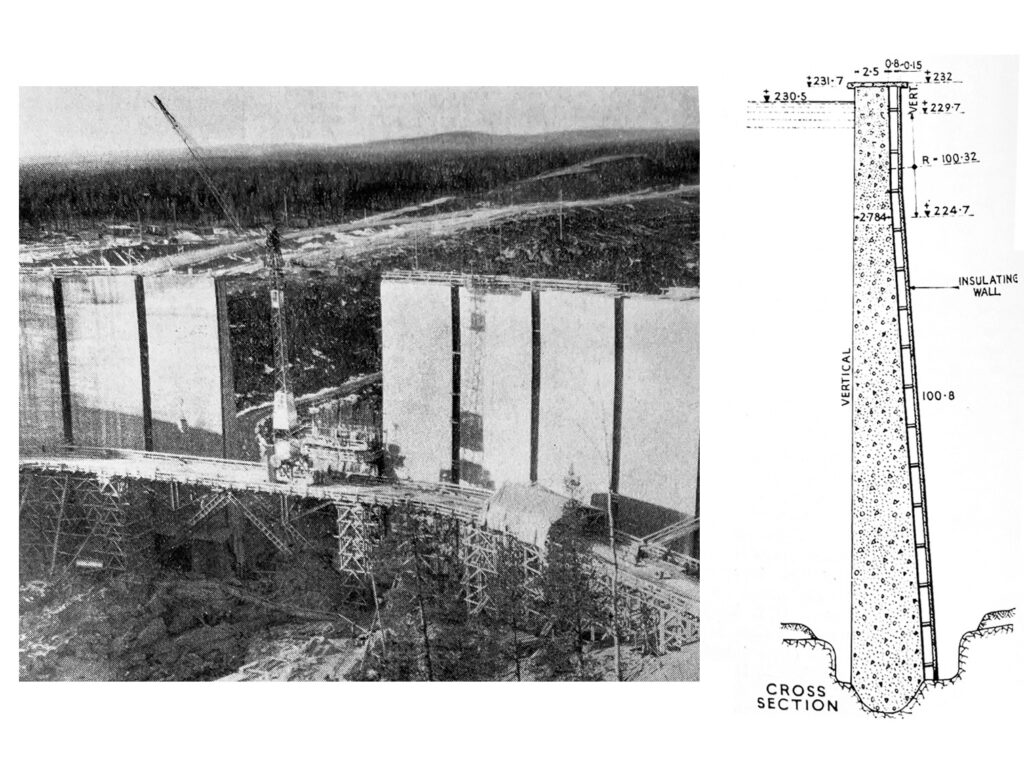
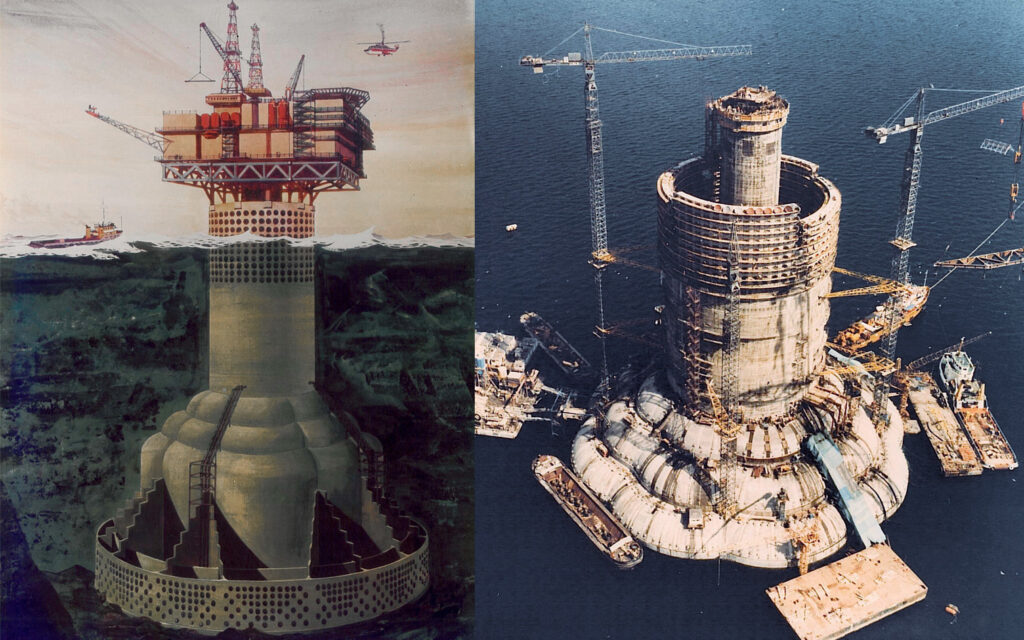
Ninian Central Oil Platform, Loch Kishorn, Scotland
Slipforming of the gravity structure. At the time, the world’s largest of its type (440,000 tons). 1950 nos slipform jacks were used.
Total height 237 m, slipformed up to level 160 m.
Bygging & Uddemann merges into Bygging-Uddemann AB
In order to utilize maximum capacities out of the mutual experiences AB Bygging and Uddemann Byggteknik AB was merged into one.
Incremental Bridge Launching Method
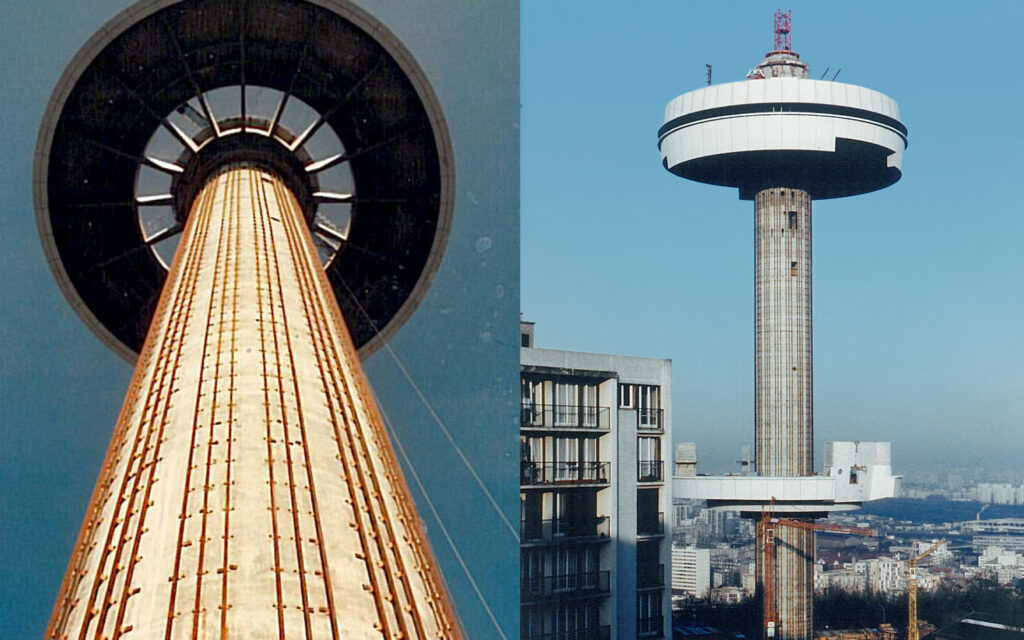
TDF-tower, Romainville, France
Slipforming of TDF-tower (Radio & TV) in Romainville, France. 141 meters high, slipforming up to level 108 m.
Heavy Lifting of four platforms weighing from 880 to 2310 tons.
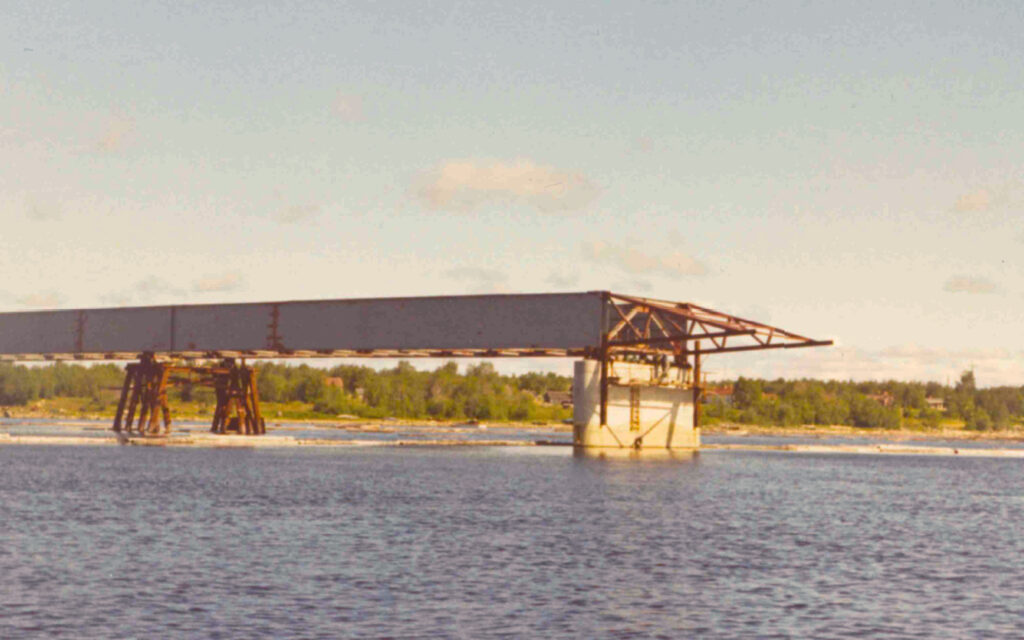
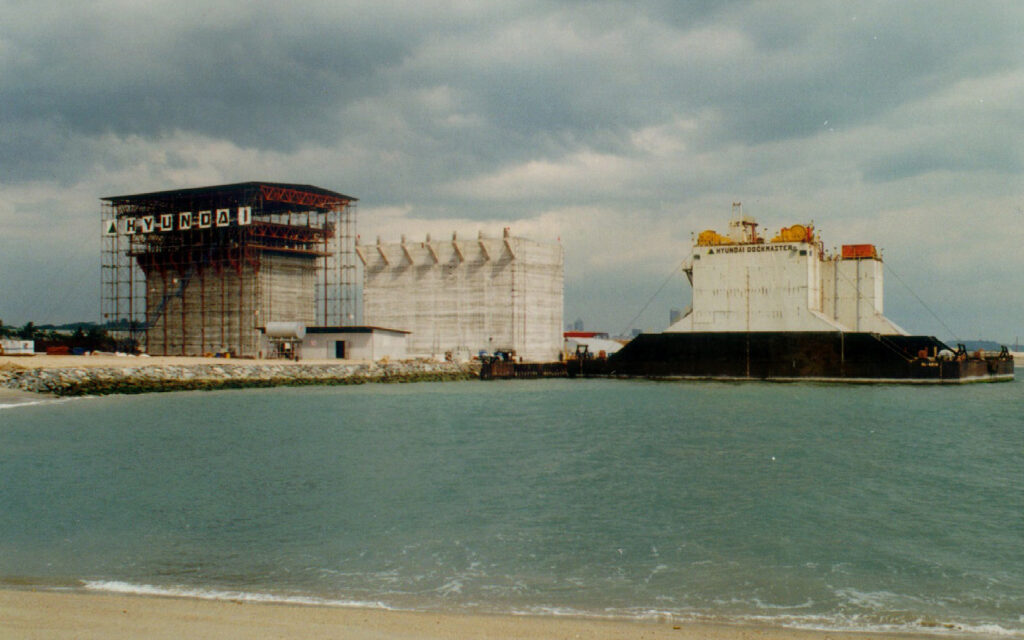
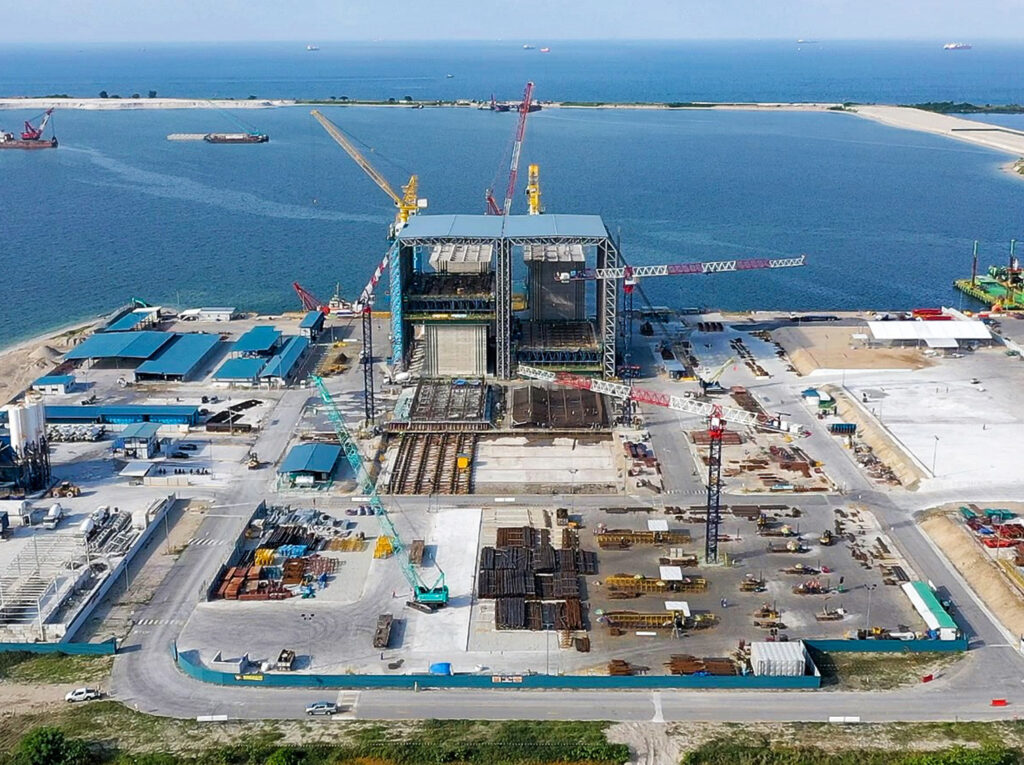
Method for Serial Production of Concrete structures
During the mid-90s, the company develops its method for serial production of concrete structures. Gantry slipform has been used in previous projects, but now the method is refined and the first generation of our skidding system “The CCV-system” is launched. The system was initially used for construction of caissons for ports and land reclamations.
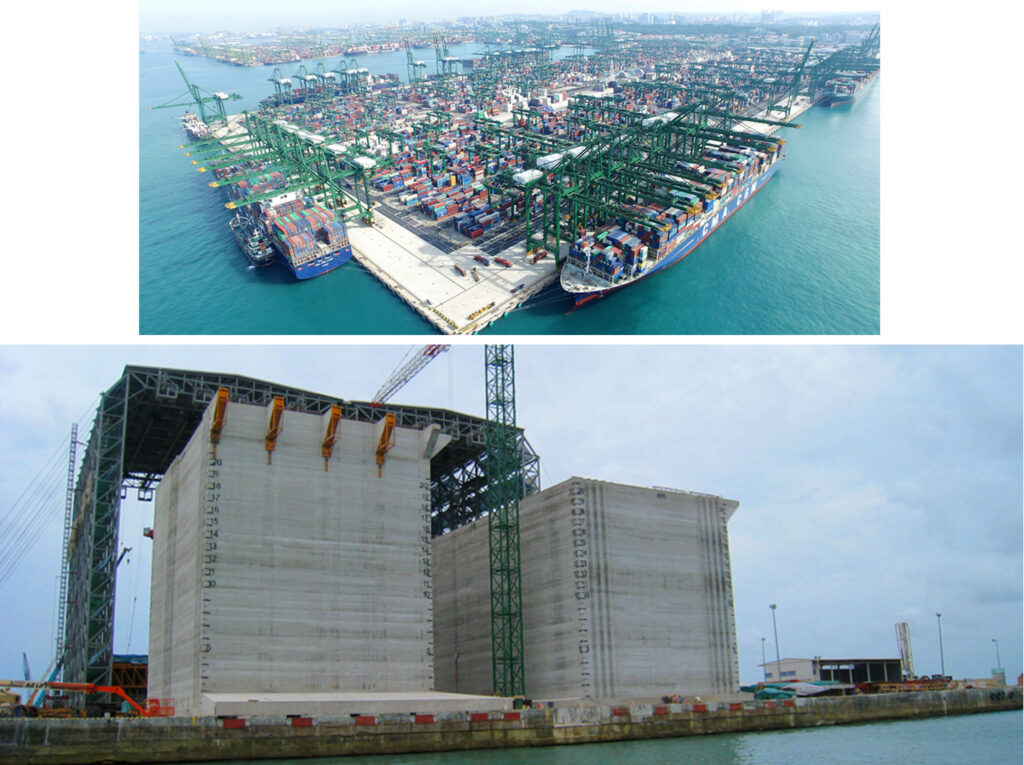
Pasir Panjang Container Terminals, Singapore
The projects in Pasir Panjang took place in two different phases between 1996 and 2010. During these a total of 238 caissons were produced using our gantry slipform method and transferred out to sea using our skidding technology.
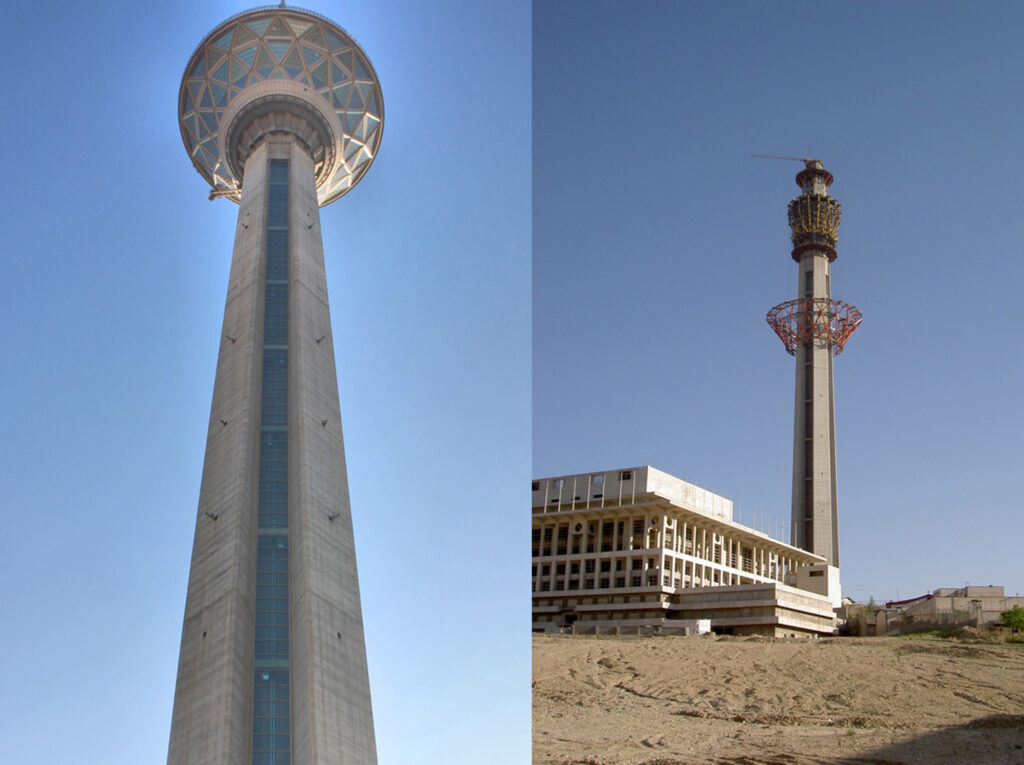
Milad Tower, Teheran, Iran
Slipforming of shaft with simultaneous lifting of tower crane. The outer walls are tapered and leaning inwards at the same time.
Our heavy lifting technology was also used to lift the tower head and antenna.
Total height 435m, slipformed to level 320m. Construction of the shaft started January 1999. Lifting of antenna was completed in 2006.
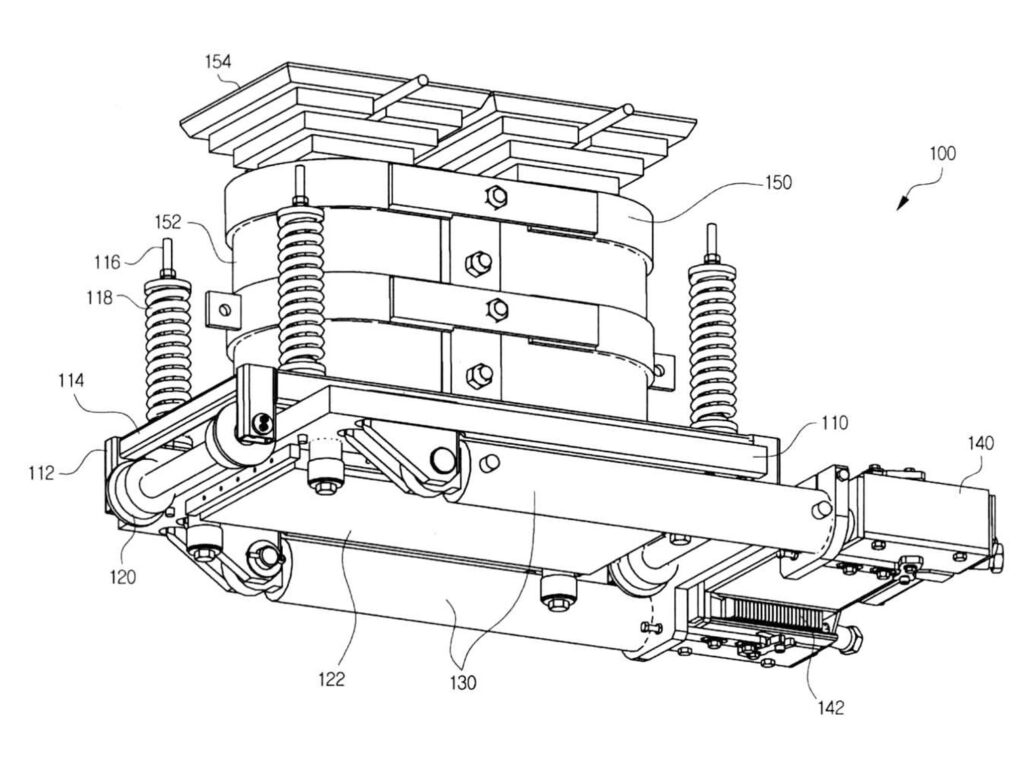
Invention of the IP-CCV unit
Our skidding method as it is designed today was developed in 2004. Lifting and horizontal movement were put together in one unit (the IP-CCV-unit). The IP-CCV-unit operates over steel tracks via low-friction plastics and epoxy-treated sliding surfaces. The greatest strenghts of the method are simplicity and durability.
We have now experienced over 1000 successful skidding operations with transfer loads from 3000 up to 6000 tons.
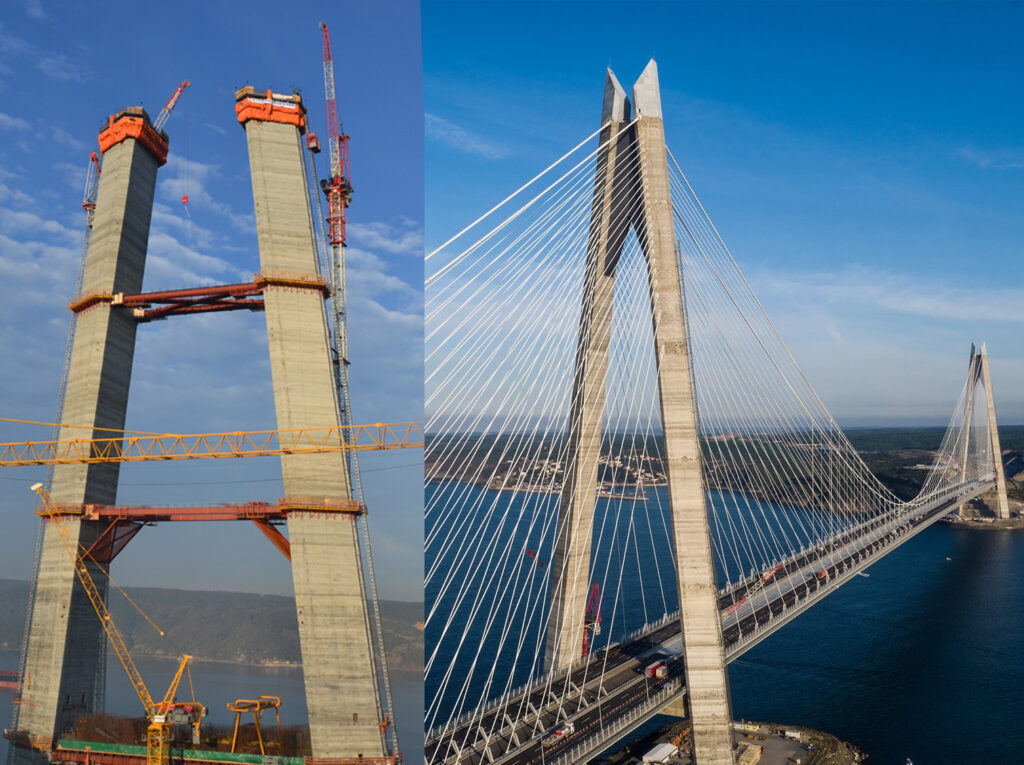
3rd Bosphorus Bridge, Istanbul, Turkey
The longest combined motorway/railway bridge in the world, and the world’s ninth longest suspension bridge, with highest pylons in the world (322m).
Slipforming of 4 pylons up to level 208m.
Tuas Container Terminal, Singapore (Finger 1, 2 & 3)
The Tuas Container Terminal projects took place in three different phases between 2015 and 2020. During these a total of 539 caissons were produced using our gantry slipform method and transferred out to sea using our skidding technology.
Development of Heavy Duty Slipform System
Our Heavy Duty Slipform System is developed to be extra rigid and at the same time very time efficient for repeated dismantling and re-assembly works.
This system allows for large cast-in items, as the distance between yokes are up to 3,5m, instead of more common 1,5-2m distance. The heavy duty yokes, with clearance of 1100mm for horizontal installation of rebar, provides a very efficient and convenient workplace for concrete and reinforcement workers.
The Heavy Duty Slipform set-up uses our strongest slipform jack, the R72 (22-ton jack) which can be positioned almost anywhere due to a very strong upper deck structure which supports the complete slipform. Instead of having to position one (or two) jack(s) at each yoke position, as with traditional slipform set-up.
Development of Mega Gantry Slipform
Our Mega Gantry Slipform venture targets the timely and budget-friendly delivery of concrete floaters for offshore wind. Building on established construction methods, our Mega Gantry System allows slipform operations with truss spans up to 65 meters (standard up to 36 m). This advanced system is pivotal for floating wind projects, symbolizing our commitment to efficient offshore construction.